Proto Manufacturing is a fundamental aspect of modern industry, involving the creation of prototypes for new products. The field plays a crucial role in the development and testing of innovative ideas before full-scale production. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of prototyping, exploring its history, job roles, career paths, education requirements, skills needed for success, industry trends, and networking opportunities.
Proto Manufacturing has a rich history that dates back to the early days of industrialization. Initially, prototypes were crafted by hand, requiring a great deal of skill and craftsmanship. However, with advancements in technology, Proto Manufacturing has evolved significantly. Today, computer-aided design (CAD) software and 3D printing have revolutionized the process, making it more efficient and precise than ever before.
For those looking to pursue a career in prototyping, there are various entry-level positions available, such as Technician or Assistant roles. As professionals gain experience and expertise, they can advance to mid-level positions like Engineer or Designer. Leadership roles, such as Manager or Director, provide opportunities for those seeking to take on greater responsibilities and lead teams in the field.
To excel in prototyping, individuals typically need a bachelor’s degree in engineering, design, or a related field. Certification programs, such as those offered by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) or the Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME), can enhance one’s qualifications and credibility in the industry. Continuing education options, such as workshops and seminars, are also available to stay current on the latest trends and technologies in prototyping.
Success in prototyping requires a combination of technical skills, such as proficiency in CAD software and 3D printing technology, as well as soft skills like communication and teamwork. Attention to detail, problem-solving abilities, and a strong work ethic are qualities that can set professionals apart in this competitive field.
The field of prototyping is constantly evolving, with advancements in technology driving innovation and efficiency. 3D printing has revolutionized the way prototypes are created, offering greater customization and speed in the production process. The future outlook for careers in prototyping is promising, with continued growth in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. Emerging opportunities in areas like virtual prototyping and rapid prototyping present exciting possibilities for professionals in the field.
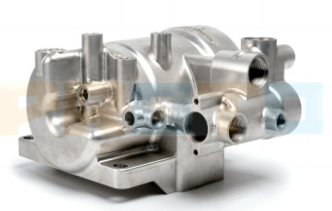
Networking is crucial for success in prototyping, as it allows professionals to connect with industry experts, share knowledge, and discover new opportunities. Professional organizations, such as the prototypingManufacturing Association (PMA) and the Society of Proto Engineers (SPE), provide valuable resources and networking events for professionals in the field. Staying updated on industry trends through conferences, webinars, and trade shows is essential for professional development and career advancement.
In conclusion, prototyping offers a dynamic and rewarding career path for individuals interested in innovation and design. From entry-level positions to leadership roles, there are a variety of opportunities available for those looking to unleash their potential in this exciting field. By acquiring the necessary skills, education, and experience, professionals can thrive in prototyping and contribute to the future of industry innovation. Take the next step towards a promising future in Proto Manufacturing and explore the endless possibilities that await.